The Complete Guide to Application Scalability: When Your App Outgrows Its Server
The Complete Guide to Application Scalability: When Your App Outgrows Its Server
Picture this: It's 2 AM, and your phone is buzzing with alerts. Your carefully crafted app, which worked perfectly during development, is now crawling under real user load. Sound familiar? You're not alone. Every successful application eventually faces this crossroads—the moment when growth becomes both a blessing and a technical challenge.
I've been through this journey multiple times, and today I want to share everything I've learned about scaling applications effectively. Whether you're a startup founder watching your user base explode or a developer preparing for the inevitable growth, this guide will walk you through the practical realities of scaling.
The Scalability Wake-Up Call
Let me start with a story. Last year, I was consulting for a food delivery startup. They launched with a simple setup—one server, one database, maybe 200 orders per day. Everything worked beautifully. Then they got featured in TechCrunch.
Within 48 hours, their traffic jumped from 200 to 5,000 daily orders. The app started timing out. The database was choking. Customer complaints were flooding in. Sound dramatic? This happens more often than you'd think.
The reality is that most applications start small, and that's perfectly fine. A single server can handle thousands of users when architected well. But eventually, every growing app hits what I call the "scaling wall"—that moment when adding more users breaks things instead of growing revenue.
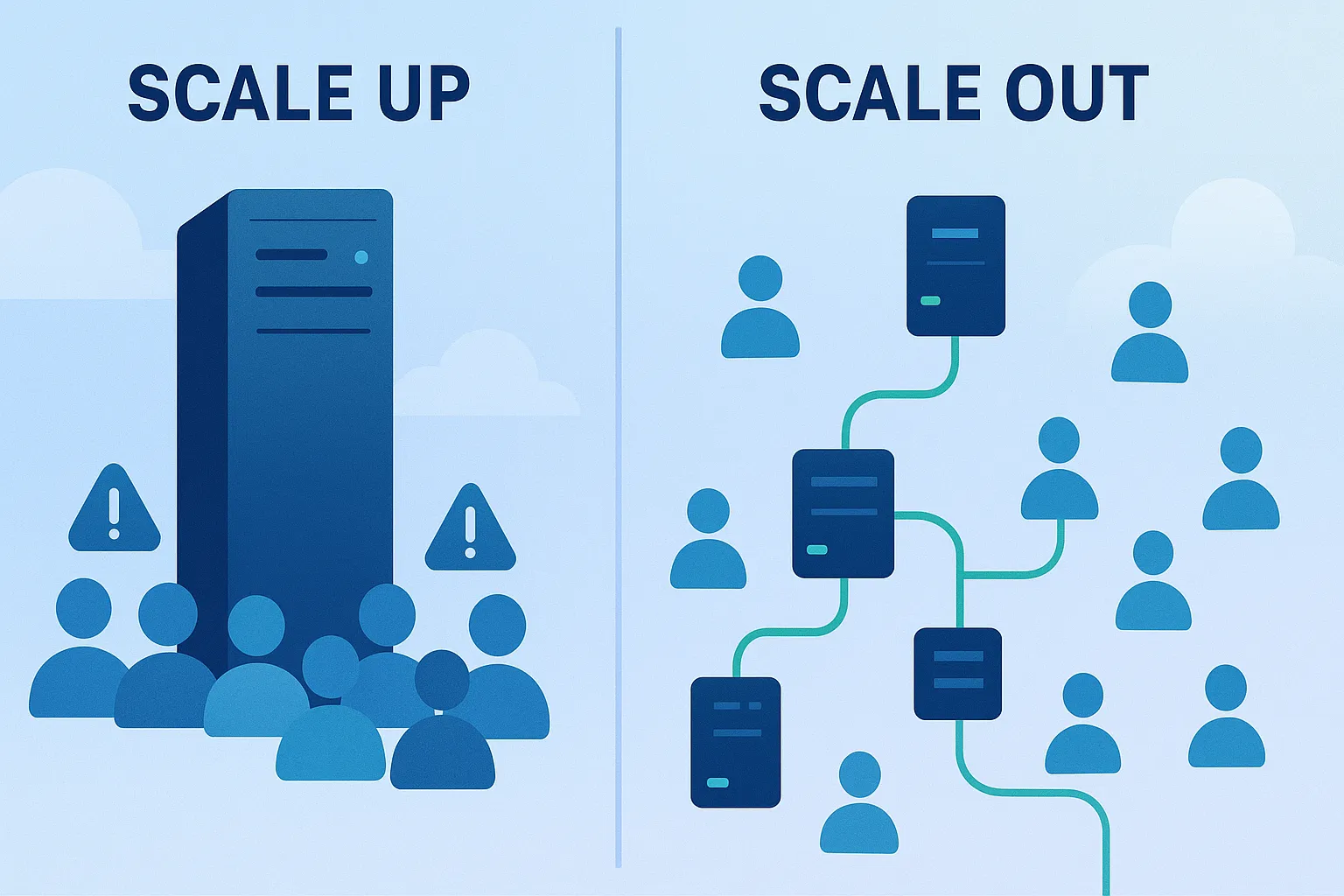
Understanding the Two Paths: Up vs. Out
When you hit this wall, you have two fundamental choices: scale up (vertical scaling) or scale out (horizontal scaling). Think of it like managing a busy restaurant.
Vertical Scaling: Making Your Chef Work Harder
Vertical scaling is like giving your chef better equipment. Instead of hiring more cooks, you buy them a faster oven, sharper knives, and a bigger workspace.
In technical terms, you're adding more power to your existing server—more CPU cores, more RAM, faster storage. It's the quickest fix when things start slowing down.
Real Example: The E-commerce Emergency
I once worked with an online bookstore that started experiencing slowdowns during their holiday sale. Their single server (4 CPU cores, 16GB RAM) was struggling with the increased traffic.
Our immediate solution? We upgraded to a beefier machine (16 cores, 64GB RAM) over a weekend. No code changes. No architectural overhaul. Just more horsepower.
The result? The site went from handling 1,000 concurrent users to comfortably serving 5,000. Crisis averted, at least temporarily.
The Sweet Spot of Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling shines in specific scenarios:
- Database servers that need consistent performance
But here's the catch—there's always a ceiling. You can't just keep adding RAM forever. At some point, you'll hit hardware limits, and the costs become astronomical. That AWS EC2 instance that costs $50/month at basic specs can jump to $3,000/month for high-end configurations.
Horizontal Scaling: Building a Team
Horizontal scaling is like hiring more chefs instead of overworking one person. You distribute the workload across multiple servers, each handling their share of requests.
This is where things get interesting (and complex). Instead of one powerful server, you have multiple smaller servers working together, coordinated by a load balancer that decides which server handles each request.
Real Example: The Learning Platform Success
One of my favorite scaling stories involves an online learning platform. They started with the typical single-server setup, but as course enrollments grew from hundreds to thousands, they needed a different approach.
Here's what we implemented:
1. Load Balancer Setup: We put three identical web servers behind an AWS Application Load Balancer 2. Database Strategy: Kept writes on the primary database but added read replicas for course content and user profiles 3. Auto-Scaling: Configured the system to automatically add servers during peak hours (typically evenings when students studied)
The magic happened during exam season. Traffic increased 10x overnight, but instead of crashing, the system automatically spun up additional servers. When the rush died down, it scaled back down, saving money.
Reading the Warning Signs: When to Scale
The tricky part isn't how to scale—it's knowing when. I've learned to watch for these telltale signs:
Performance Indicators
- Response times creeping up: What used to take 200ms now takes 2 seconds
User Experience Signals
- Timeout complaints: Users reporting that pages won't load
Business Impact Metrics
- Conversion rates dropping: Technical issues affecting sales
The Cost Reality Check
Let's talk money, because scaling decisions are ultimately business decisions.
Vertical Scaling Economics
I recently helped a client analyze their scaling costs. Their current setup:
That's a 64x cost increase for roughly 8x performance improvement. The economics don't scale linearly.
Horizontal Scaling Math
Compare that to horizontal scaling:
Linear cost scaling, plus you get redundancy. If one server fails, you still have nine others running.
A Real-World Scaling Journey
Let me walk you through a complete scaling journey I managed for a food delivery app. This will give you a practical framework for your own scaling decisions.
Starting Point: The Single Server Days
- Load: 500 orders per day
Month 6: The Growth Problem
- Load: 3,000 orders per day
Quick Fix: Vertical Scaling
We upgraded to a more powerful server:
This bought us time, but we knew it wasn't sustainable.
Month 12: The Horizontal Transformation
With orders approaching 10,000 per day, we implemented a full horizontal scaling strategy:
1. Web Tier: Three application servers behind AWS Application Load Balancer 2. Database Tier: Primary for writes, two read replicas for queries 3. Caching Layer: Redis cluster for session data and frequently accessed menus 4. Auto-scaling: Kubernetes deployment that automatically adjusts server count based on load
The Results
- Capacity: Now handles 25,000+ orders per day
Choosing Your Scaling Strategy
Here's the decision framework I use with clients:
Start with Vertical When:
- You need a quick fix to immediate performance issues
Move to Horizontal When:
- You're planning for significant, unpredictable growth
The Hybrid Approach
In reality, most successful scaling strategies use both. You might vertically scale your database servers while horizontally scaling your web servers. The key is understanding which components benefit from which approach.
Common Scaling Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
After years of scaling applications, I've seen the same mistakes repeated:
Mistake 1: Premature Optimization
Don't build for 10 million users when you have 1,000. Scale based on actual needs, not hypothetical futures.
Mistake 2: Ignoring Bottlenecks
Adding more web servers won't help if your database is the limiting factor. Always identify the actual bottleneck first.
Mistake 3: All-or-Nothing Scaling
You don't need to rebuild everything at once. Scale incrementally, component by component.
Mistake 4: Neglecting Monitoring
You can't scale what you can't measure. Implement comprehensive monitoring before you need to scale.
Tools and Technologies That Make Scaling Easier
Monitoring and Alerting
- New Relic or DataDog: Application performance monitoring
Load Balancing
- AWS Application Load Balancer: Managed solution with auto-scaling integration
Container Orchestration
- Kubernetes: Industry standard for container orchestration
Database Scaling
- Read Replicas: For read-heavy workloads
Preparing for Future Scale
The best scaling strategy is the one you plan for before you need it. Here's how to build scale-ready applications:
Design Principles
1. Stateless services: Store session data externally (Redis, database) 2. Microservices architecture: Break monoliths into scalable components 3. Database design: Plan for read replicas and potential sharding 4. Caching strategy: Implement caching at multiple layers
Infrastructure as Code
Use tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation to define your infrastructure. This makes scaling repeatable and reduces human error.
Continuous Integration/Deployment
Implement CI/CD pipelines that can deploy to multiple environments consistently.
The Bottom Line
Scaling isn't just a technical challenge—it's a business enabler. The difference between a startup that crashes under success and one that thrives often comes down to scaling strategy.
Remember:
Every application's scaling journey is unique, but the principles remain constant. Whether you're handling hundreds or millions of users, the key is understanding your specific needs and choosing the right approach for your situation.
The next time you see those performance alerts at 2 AM, you'll know exactly what to do. And more importantly, you'll have the architecture in place to handle whatever growth comes next.